Case 1: Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
Clinical History
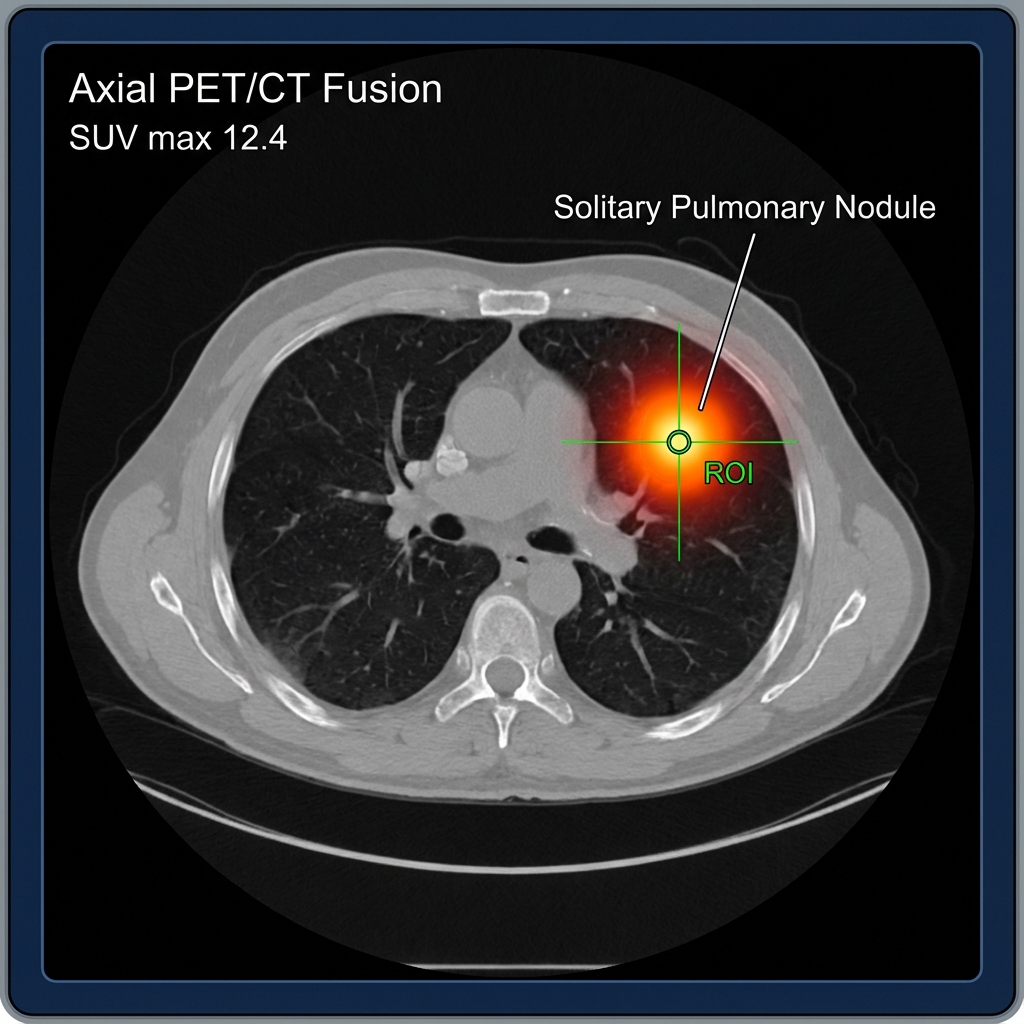
Patient: 58-year-old female History: Incidental 1.5 cm right upper lobe nodule found on screening CT Indication: Characterization of Solitary Pulmonary Nodule (SPN)
Imaging Findings
Technique: F-18 FDG PET/CT (Vertex to mid-thighs)
PET/CT Fusion
- Located in the right upper lobe, there is a hypermetabolic nodule measuring 1.6 x 1.5 cm.
- SUV max: 12.4
- No hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
- No distant metastasis.
Diagnosis
Findings:
- Intensely hypermetabolic pulmonary nodule (SUV > 2.5 is typically suspicious).
- Absence of benign calcification patterns.
Interpretation: High probability of malignancy. Biopsy is recommended.
Pathology Follow-up: Adenocarcinoma.
Learning Points
- SUV Thresholds: While SUV > 2.5 suggests malignancy, overlap exists with granulomatous disease (e.g., Histoplasmosis, TB).
- SPN Evaluation: PET/CT has high sensitivity (~95%) for nodules > 1 cm.
- False Negatives: Can occur with carcinoid tumors and mucinous adenocarcinomas (low metabolic activity).
- False Positives: Infection, inflammation, granulomas.